
**TL;DR**
Real time data is becoming the operating system for modern teams. A scraper API gives technical experts a simple and reliable way to pull fresh data without building heavy infrastructure. It handles complex websites, rotating proxies, JavaScript rendering, CAPTCHAs, and structured outputs so your workflows stay clean and fast. If you work with competitive intelligence, pricing, ecommerce, research, or operational analytics, a scraper API keeps your pipelines accurate and current. This blog breaks down how it works, why it matters, and where it gives the biggest advantage.
An Introduction to Scraper API
Every technical team eventually hits the same roadblock. You can build a scraper that works for a day or a week, but the moment a layout shifts or a website tightens its defences, the whole system slips. What should be a simple stream of data becomes a cycle of fixing scripts and chasing errors.
A scraper API changes that experience entirely. Instead of maintaining your own crawling stack, you call an endpoint and get clean structured data back. It feels like switching from running your own servers to using cloud computing. The complexity is still there under the hood, but you never have to touch it.
Real time access to this data is where the value really shows. Markets shift quietly and then all at once. Prices move. Products appear and disappear. Customer sentiment jumps. Competitors adjust their strategy overnight. When your system listens to these changes the moment they happen, your decisions get sharper and your forecasts get more honest.
Throughout this article, we will look at how scraper APIs work, what features matter, and why technical experts rely on them for fast, accurate and compliant data acquisition. Once you see the difference between manual scraping and API based extraction, it becomes clear why scraper APIs are now the backbone of modern data pipelines.
How a Scraper API Works Behind the Scenes
When you send a request to a scraper API, it looks simple on the surface. You hit an endpoint. You get structured data back. But under that calm surface, a lot happens in milliseconds.
A scraper API behaves like a small army of browsers working on your behalf. It loads the page, waits for scripts to run, handles redirects, interprets dynamic blocks, and collects only the pieces you asked for. All of this is wrapped inside an infrastructure that has one goal. Deliver clean data every time.
Most APIs follow a predictable internal workflow. It begins by receiving your request with the URL and parameters you want. The system then decides which proxy location should fetch that page. This helps avoid being blocked and ensures you see the correct version of the site, especially for geo specific data.
The API then spins up a headless browser. Think of this as a quiet version of Chrome running without a screen. It loads the page fully and waits until every script, widget, and product card is visible. You are not dealing with raw HTML here. You are looking at the final rendered page that a real visitor sees.
Next comes the extraction phase. The API looks for the exact elements you requested. It reads through product details, prices, titles, reviews, stock levels, menu paths, or whatever you defined. It converts that messy structure into neat JSON that fits your pipeline.
If the page throws a CAPTCHA or a challenge, the API has a built in routine to solve or bypass it. If the site refuses the request or loads an error, the system automatically retries from a different proxy or uses a backup method to fetch the data. You do not see any of this. You just receive the final answer.
Behind the scenes there is also constant validation. The API checks the fields you asked for, confirms that the output fits your schema, and removes empty or broken entries. This prevents the most common problem in scraping which is silent data drift that breaks dashboards and models.
A good scraper API becomes invisible after a while. Technical teams stop thinking about failures. Analysts stop worrying about missing values. Engineers stop rewriting brittle scripts. The API absorbs all that complexity so your time shifts from fixing problems to using the data that arrives on schedule and at scale.
Want reliable, structured Temu data without worrying about scraper breakage or noisy signals? Talk to our team and see how PromptCloud delivers production-ready ecommerce intelligence at scale.
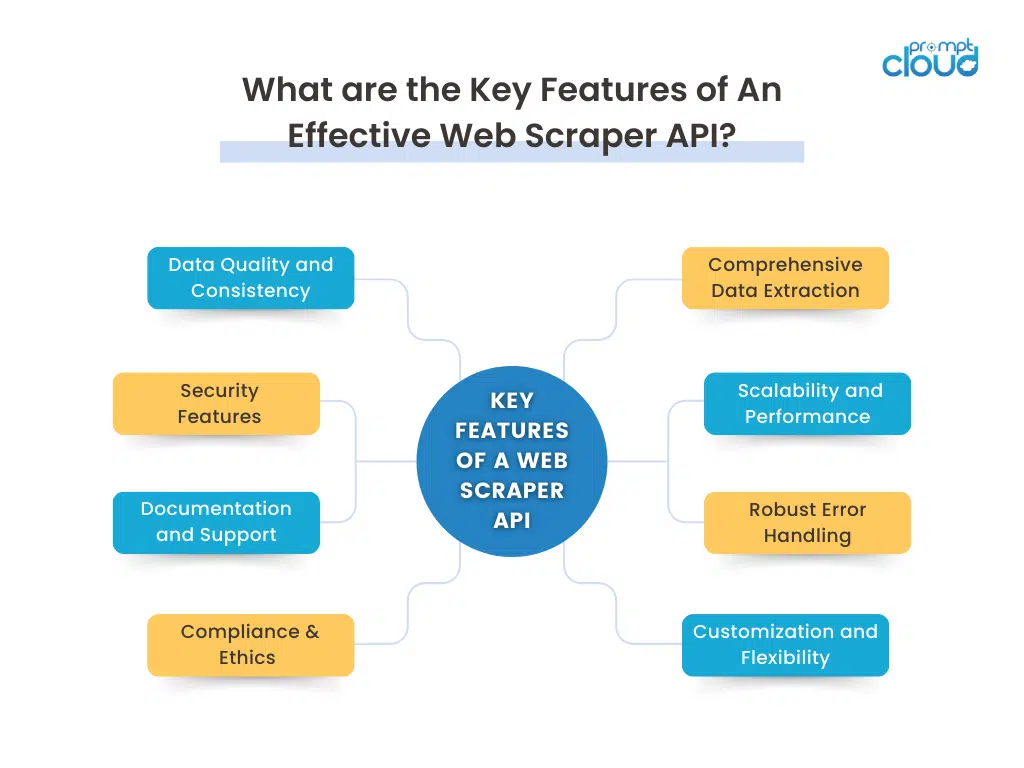
The Key Features That Make a Scraper API Reliable
Not every scraper API is built for production work. On paper most tools look similar. In practice some quietly fall apart the moment traffic spikes or a target site changes its layout. Technical teams care less about flashy features and more about what holds up on a busy Tuesday morning.
Here are the traits that separate a reliable scraper API from the rest.
1. Strong page rendering and extraction
A good scraper API can handle the kind of sites your team actually cares about. That usually means JavaScript heavy pages, nested elements, and content that appears only after user-like actions.
- Handles JavaScript and dynamic widgets
- Targets specific elements such as product cards or review blocks
- Returns clean JSON that fits directly into your pipeline
When this part is weak, engineers spend time patching selectors and analysts spend time cleaning messy exports. When it is strong, everyone simply trusts the data.
2. Built for scale, not just demos
A scraper api that works for ten URLs is easy. The real test comes when you move to thousands of pages across countries and time zones.
You want to see:
- High request throughput without random slowdowns
- Support for parallel jobs and batch endpoints
- Smart rate limiting so you stay under the radar of target sites
This is what lets your team schedule hourly or event driven runs without worrying that one new project will break everything else.
3. Real error handling, not silent failures
In scraping, things go wrong all the time. Layouts change. Networks drop. A site throws a new challenge page. A reliable scraper API assumes this and plans for it.
Look for:
- Clear status codes and error messages
- Automatic retries with backoff
- Fallback strategies such as alternate selectors or backup regions
Most importantly, the API should never fail quietly. If a field cannot be extracted, you need to know. That transparency keeps your models and dashboards honest.
4. Flexible control for technical teams
A strong scraper api gives experts room to tune behaviour without forcing them to build everything from scratch.
Examples of useful controls include:
- Query parameters for location, device type, or language
- Custom extraction rules or templates for specific page types
- Options for scheduling, frequency, and priority
The goal is not to expose every internal knob. It is to give you enough control that the API fits your stack instead of forcing you into a rigid pattern.
5. Data quality baked into the pipeline
Speed is pointless if the output cannot be trusted. Reliable scraper APIs treat data quality as a first class feature rather than an afterthought.
This often includes:
- Field level validation for types like price, date, rating, stock flag
- Normalisation of formats such as currencies, units, and timestamps
- De duplication so you do not count the same item ten times
When quality checks happen upstream, your team spends less time cleaning and more time analysing.
6. Security and privacy by default
Any scraper api that touches customer environments or sensitive contexts needs a clear security story.
You should see:
- Encrypted requests and responses
- Proper handling of keys and credentials
- IP rotation that respects privacy and compliance needs
For larger organisations this is also where vendor reviews, SOC reports, and data handling policies come into play. Trust is built here long before the first request is sent.
7. Documentation and human support
A scraper API lives or dies by how fast someone new can use it. Good documentation and responsive support save weeks of trial and error.
That usually means:
- Clear examples in common languages
- Copy paste ready request and response samples
- Direct access to a support team that understands scraping, not just generic tickets
When an edge case appears, you want to talk to people who have seen similar patterns across many clients and targets.
8. Respect for rules and compliance
Finally, a reliable scraper api helps you do the right thing. It should make it easier to stay aligned with robots rules, terms of use, and relevant laws rather than leaving everything to chance.
Features that help here include:
- Built in respect for crawl policies and rate limits
- Options for regional routing to align with data regulations
- Clear guidelines on permitted use cases
This is how technical teams scale scraping without putting their organisation at risk.
When these pieces come together, a scraper API stops feeling like a fragile script and starts behaving like core infrastructure. You can plug it into new projects with confidence, knowing that the same engine is looking after scale, quality, and compliance while your team focuses on what the data means.

How Technical Teams Actually Use a Scraper API
In practice, using a scraper api looks less like a one off script and more like a small product inside your stack. Technical teams follow a repeatable pattern so that the data they pull today will still work quietly a month from now.
It usually starts with choosing the right scraper api for the job. Teams look at supported targets, locations, authentication, request limits, and pricing. Once a candidate looks promising, engineers dive into the documentation to understand endpoints, parameters, and response formats before writing a single line of integration code.
Next comes authentication. Most scraper APIs rely on API keys or tokens. These are stored securely in environment variables or secret managers, never hard coded in scripts. A quick series of smoke tests with tools like curl or Postman helps confirm that requests, headers, and query parameters are all wired correctly.
Once the basics are stable, teams design how each request should behave. They define target URLs, filters, pagination rules, and any custom extractor templates the scraper api supports. At this point they also decide how the response will map to internal models so the output fits their warehouse or data lake without extra cleaning work.
Here is how that flow usually looks when you break it into phases.
| Phase | Goal | What you configure in the scraper api |
| Discovery and selection | Confirm the tool fits your use case | Targets, supported sites, locations, rate limits |
| Authentication and testing | Prove the connection is stable | API keys, headers, sample URLs, basic success and error checks |
| Request design | Shape the data you want | URL patterns, query params, pagination, extraction templates |
| Parsing and mapping | Fit data into your schema | Field mappings, type casting, normalisation rules |
| Scheduling and monitoring | Keep data fresh and healthy | Frequency, retry rules, alerting, logging preferences |
After the design phase, integration moves into your normal pipeline tooling. Engineers hook the scraper api into jobs that run on Airflow, cron, or another orchestrator. Responses are validated, transformed, and loaded into storage where analysts, models, or dashboards can reach them.
The final piece is monitoring. Teams track request success rates, latency, field completeness, and schema changes. When a target site shifts layout or adds new defences, alerts fire before the change corrupts downstream reports. Over time this turns scraping from a fragile side project into a dependable data service that behaves like any other production dependency.
Used this way, a scraper api becomes the quiet backbone of many workflows. You call it the same way every day, it returns clean results in the same shape, and your team can focus on what the data is saying rather than how it was collected.
The Practical Benefits of Using a Scraper API
Once a scraper api becomes part of your workflow, the advantages show up quickly. Some are obvious, like saving time or avoiding manual extraction. Others appear only after weeks of steady use when you notice how much smoother your pipelines run and how much less maintenance pulls your team away from real work.
Below is a clearer and more grounded look at the benefits, written the way technical teams actually experience them.
1. Efficiency that compounds over time
A scraper api automates a task that many teams still treat as an internal project. Instead of spinning up headless browsers, managing IP pools, or cleaning noisy HTML, your system calls an endpoint and moves on.
You get:
- Faster data collection without engineering overhead
- Automated handling of pagination, redirects, and dynamic sections
- Stable performance even as volume increases
What starts as a small convenience turns into hours saved every week.
2. Accuracy you can trust
Good scraper APIs validate and normalise fields before returning them. That means fewer missing prices, malformed dates, random characters, and broken fields that crash dashboards.
This leads to:
- Cleaner inputs for analytics and modelling
- Fewer surprises from silent data drift
- Consistent structure that does not change without notice
- Accuracy is not just about correctness. It is about predictability.
3. Flexibility across use cases
A single scraper api can power many different teams. Engineers use it for automation, analysts use it for research, and product managers use it to monitor competitors.
Scraper APIs usually support:
- JSON, CSV, XML and other formats
- Multiple device types or locations
- Custom selectors or templates for structured extraction
- This flexibility keeps the tool useful even as your needs evolve.
4. Lower operational cost
Running your own scraping setup is expensive. You need proxies, compute, storage, queueing, monitoring, retries, and constant upkeep. A scraper api absorbs all of that cost into a predictable usage model.
Teams avoid paying for:
- Large proxy pools
- Browser orchestration and maintenance
- Continuous debugging when a site changes overnight
- The savings often show up first in engineering hours, then in infrastructure.
5. Built in compliance guardrails
Scraper APIs help teams stay aligned with best practices and legal expectations. Good vendors design guardrails that protect both the user and the target websites.
These guardrails include:
- Rate limiting aligned with robots rules
- IP rotation that respects regional regulations
- Secure handling of requests and encryption of responses
Compliance becomes something you inherit instead of something you chase.
6. Real time performance that supports live decisions
Businesses today react to things that change quickly. Prices shift. Product availability changes. Reviews spike or drop. A scraper api lets you capture these shifts as they happen.
Here is a simple comparison that teams often use when deciding whether they need real time feeds.
| Requirement | Manual scraping setup | Scraper API |
| Freshness | Hours or days | Minutes or seconds |
| Handling sudden volume spikes | Needs reconfiguration | Built in elasticity |
| Tracking time sensitive events | Requires custom scripts | Available out of the box |
| Patching broken selectors | Frequent manual fixes | Automated fallback systems |
When your data arrives quickly and reliably, the insights do too. That is what makes scraper APIs valuable across industries where timing changes the outcome.
How Scraper APIs Drive Innovation Across Industries
When teams start using a scraper api consistently, something interesting happens. The data stops being a background utility and begins shaping decisions across the organisation. Entire workflows get sharper because fresh information flows in without friction. Different teams interpret that data in their own way, which is why scraper APIs end up powering more than just engineering tasks.
Below is a clearer look at how various industries rely on scraper APIs in ways that directly influence strategy and product direction.
1. Market research and competitive intelligence
This is the space where scraper APIs feel almost made to fit. Companies watch competitors the same way traders watch charts. Price changes, new product launches, promotional events, and shifting review sentiment appear online long before reports come out.
Scraper APIs help teams:
- Track competitor pricing and promotional cycles
- Monitor category level trends across marketplaces
- Understand how review sentiment changes after updates
- Map availability and stock outs to demand patterns
Teams often feed this data into dashboards so product and pricing leaders can read the room each morning with live context instead of stale reports.
2. Financial services and modern investment research
Financial analysts care about signals that move before the market does. Traditional data feeds give part of the picture, but web data adds texture and immediacy.
Common scraper API use cases include:
- Extracting earnings sentiment from news and investor forums
- Tracking macroeconomic indicators published across government portals
- Gathering exchange data across cryptocurrency platforms
- Monitoring shipping, trade, or commodity movements through public sources
The people who build models on top of this data depend on freshness. That is where scraper APIs give them a competitive edge.
3. E commerce and retail operations
Retailers live in fast moving environments. A small change in competitor pricing, a sudden stock out, or a shift in product reviews can ripple across customer behaviour. A scraper api lets teams listen to these signals without maintaining hundreds of scripts.
Retailers use scraper APIs to:
- Track marketplace pricing and promotional behaviour in near real time
- Monitor product visibility and ranking shifts
- Collect customer reviews at scale for sentiment and feature requests
- Predict demand changes based on competitor inventory levels
This data often sits at the heart of pricing engines and inventory forecasting models.
4. Real estate and property intelligence
Real estate professionals work with distributed and inconsistent data sources. Property listings differ in format, structure, and reliability. A scraper api gives teams a way to unify these sources without constant manual checks.
Practical applications include:
- Extracting rental and sale listings across multiple portals
- Tracking how prices fluctuate in specific neighbourhoods
- Monitoring availability and supply cycles
- Collecting leads and owner contact details where permitted
Many real estate analytics tools today are powered by clean, API delivered listing data behind the scenes.
5. Academic, policy, and social science research
Researchers depend on large bodies of public information. Scraper APIs help them collect this data consistently and repeatedly so their studies rely on stable inputs.
Common patterns include:
- Sentiment analysis on public discussions or news cycles
- Identifying trends in academic citations or publication networks
- Analysing behavioural patterns across community forums
- Monitoring policy related content published across government domains
A scraper api reduces the manual burden and ensures the dataset remains current throughout long research cycles.
6. Travel and hospitality analytics
Travel demand shifts quickly. Prices move every hour. Availability changes as booking windows fluctuate. A scraper API makes it possible to track this constantly changing environment without dedicating a team to upkeep.
Teams rely on scraper APIs for:
- Price comparison across booking platforms
- Monitoring hotel availability and seasonal fluctuations
- Capturing customer reviews and rating shifts
- Tracking competitor offers and dynamic packages
This gives hotels, travel platforms, and agencies a more realistic view of demand in the moment rather than relying only on historical patterns.
7. Automotive, logistics, and mobility
This is a fast growing category where online data tells you almost everything about market readiness. From EV listings to charging availability, scraper APIs help analysts surface insights that previously required manual research.
Typical workflows include:
- Tracking new and used vehicle inventory
- Monitoring charging station density and uptime
- Extracting feature comparisons across manufacturers
- Reviewing owner sentiment across forums and review websites
Much of the innovation in EV analytics tools today comes from combining scraper API data with internal operational metrics.
When You Should Use a Scraper API Instead of Building In House
Most teams reach a turning point in their scraping journey. The internal scripts that seemed manageable at the start begin to drain time. Proxies need rotation. Websites add new defences. Layouts shift without warning. Engineers patch things late at night. Analysts wait for updated feeds. Dashboards break quietly. The entire workflow becomes unpredictable.
A scraper api becomes the better path when the cost of maintaining your own infrastructure outweighs the value of controlling every piece of it. Below are the moments when teams usually decide that building in house no longer makes sense.
1. When the target websites change often
If the sites you rely on update layouts, switch frameworks, or add anti bot layers regularly, an in house scraper becomes a constant repair job. Scraper APIs carry this burden for you by updating extraction logic and fallback systems across all clients.
2. When you need consistent real time data
If your insights, models, or monitoring tools depend on fresh data, reliability matters more than custom code. Scraper APIs maintain uptime, rotate IPs, solve challenges, and scale automatically so you never fall behind.
3. When your team is small or already stretched
Engineers rarely join a company to maintain scrapers. When internal priorities shift to product development, security, or infrastructure improvements, data collection gets pushed aside. A scraper api lets you keep the pipeline running even when bandwidth is limited.
4. When you need geographic diversity
Running a proxy network across regions is expensive and operationally heavy. Scraper APIs offer built in location routing so you can fetch data as a user in the US, UK, Brazil, Germany, or India without maintaining a global footprint.
5. When you operate in a compliance sensitive environment
If you work in finance, healthcare, enterprise governance, or any field with legal oversight, you need guardrails. Scraper APIs enforce rate limits, honour robots rules, encrypt requests, and maintain audit trails. This is difficult to replicate internally with the same rigour.
6. When downtime is no longer acceptable
Internal scrapers are brittle. They fail silently or break at inconvenient times. A scraper api offers stability, monitoring, automated retries, and predictable behaviour. When your data pipeline becomes a core dependency, predictability matters more than control.
7. When you want to focus on analysis, not infrastructure
Most organisations want insights, not a scraping farm. If your goal is to improve pricing decisions, monitor competitors, study sentiment, or analyse availability, your time is better spent interpreting data rather than collecting it.
Building a Practical Path Forward with a Scraper API
Most data teams do not adopt a scraper api because it feels trendy. They adopt it because the old way of collecting data eventually hits a limit. Internal scripts break too often. Proxy pools get expensive. Engineers lose time to patching instead of building. Dashboards fall behind because the data feeding them is no longer fresh. At some point, the workflow becomes too fragile to support the decisions that depend on it.
A scraper api gives you a way out of that cycle. It removes the heavy lifting that usually slows teams down and replaces it with a service that delivers the same dataset every time you call it. Consistency becomes the real win. Instead of worrying about whether the next run will fail, your pipeline works the same way every day. That stability frees your team to focus on the part that actually creates value, which is understanding what the data means and using it to steer the business forward.
If your job involves watching competitors, tracking prices, studying customer sentiment, analysing listings, or monitoring market changes, the speed and reliability of a scraper api directly influence how well you can respond. Fresh data is not a luxury in these environments. It is a requirement. The teams that move quickly are the ones with a clean feed coming in at predictable intervals, not the ones waiting for someone to fix a broken selector.
The practical advantage becomes even clearer as your use cases scale. More URLs. More categories. More geographies. More frequency. An in house setup that handled a few hundred pages a day suddenly struggles at a few thousand. You could rebuild everything, expand infrastructure, and shift internal resources, but that cost grows faster than the benefits. A scraper api absorbs this expansion without forcing you to redesign your system. You increase volume, and the service takes care of the operational lift.
Even teams with strong engineering depth eventually choose a scraper api because the trade off becomes obvious. Every hour spent maintaining scrapers is an hour not spent improving models, refining pricing logic, strengthening product analytics, or shaping strategy. The opportunity cost grows quietly until it becomes hard to ignore. Outsourcing the collection layer lets the team reallocate time to the work that moves the organisation forward.
If you are looking at your own workflows and noticing these patterns, this is the moment to treat data collection as a service rather than a project. A scraper api is not about giving up control. It is about choosing stability, speed, and scalability so your organisation can act faster with fewer interruptions. It turns scraping from a side responsibility into a dependable foundation that supports research, automation, forecasting, and decision making.
In practical terms, the next steps are simple. Identify the data you need, define how often you need it, and plug a scraper api into that workflow. Once the feed stabilises, you will see the difference immediately. Clean data arrives on time. Dashboards update without gaps. Analysts stop waiting. Engineers stop triaging failures. The entire system becomes more predictable.
That is the point when teams realise that a scraper api is not just a tool. It is an operational shift that removes friction from every downstream process. It keeps your data current, your decisions grounded, and your workflows moving, which is exactly what modern organisations need as the pace of change continues to rise.
If you want to explore more…
Here are four related articles from PromptCloud that deepen your understanding of real time scraping, event driven pipelines, and ethical data collection:
- Learn how image scraping supports ecommerce AI in our guide on image scraping for ecommerce AI.
- Compare capabilities in our breakdown of Instant Data Scraper comparison for build vs buy decisions.
- See real time pipelines in action in our article on event triggered price monitoring.
- Understand the future of governance in our deep dive on machine access rules beyond robots.txt.
For authoritative guidance on designing reliable API integrations, the Mozilla Developer Network provides an in depth overview of best practices for building secure and stable HTTP request workflows.
Reference: MDN Web Docs on HTTP APIs
Want reliable, structured Temu data without worrying about scraper breakage or noisy signals? Talk to our team and see how PromptCloud delivers production-ready ecommerce intelligence at scale.
FAQs
1. What makes a scraper API different from building scrapers manually?
A scraper api handles rendering, proxy rotation, retries, and validation behind the scenes. You receive structured data consistently without owning infrastructure or fixing scripts whenever a target site changes.
2. Can a scraper API handle complex JavaScript heavy websites?
Yes. Modern scraper APIs load pages with headless browsers so dynamic elements, product cards, and script rendered content are captured exactly as a user sees them.
3. Is a scraper API suitable for real time data needs?
A scraper api is built for real time monitoring. It manages multiple concurrent requests, fallback strategies, and rapid extraction so your pipelines stay current with fast moving markets.
4. How do scraper APIs ensure data quality?
They apply validation rules, normalise fields, catch missing values, and remove duplicates before delivering results. This keeps your downstream dashboards and models accurate and stable.
When does using a scraper API become more cost effective than in house scraping?
When you need scale, geographic diversity, dynamic rendering, or high uptime. Internal maintenance costs rise quickly while a scraper api spreads that operational complexity across every client.



















