
**TL;DR**
Picking a web scraping partner in 2026 isn’t about speed or headline price. You need proof of compliance, real QA, clear SLAs for delivery, and strong security practices. This guide lays out what to check: core capabilities, support commitments, cost transparency, and an RFP you can send today. Use it to score vendors, avoid the usual failure points, and choose a managed service that meets your standards for compliance, quality, and uptime.
Why Vendor Selection in Web Scraping Has Changed
Web scraping in 2026 is no longer a side project for developers. For most enterprises, it’s the backbone of pricing automation, market research, product analytics, and AI model training. That shift has changed how vendor selection works.
Outdated checklists like “do they support headless browsers” or “can they parse JavaScript pages” are now table stakes. Today’s top companies ask:
- Can this vendor meet our data quality SLAs?
- Do they offer compliance-ready delivery with jurisdictional routing?
- What security practices protect the pipeline and output?
- Can the service scale across thousands of URLs, categories, or sites without breakage?
- What happens when something fails—who’s accountable?
This evolution means your RFP process needs to be modernized too. You’re no longer just buying scrapers. You’re selecting a data partner.
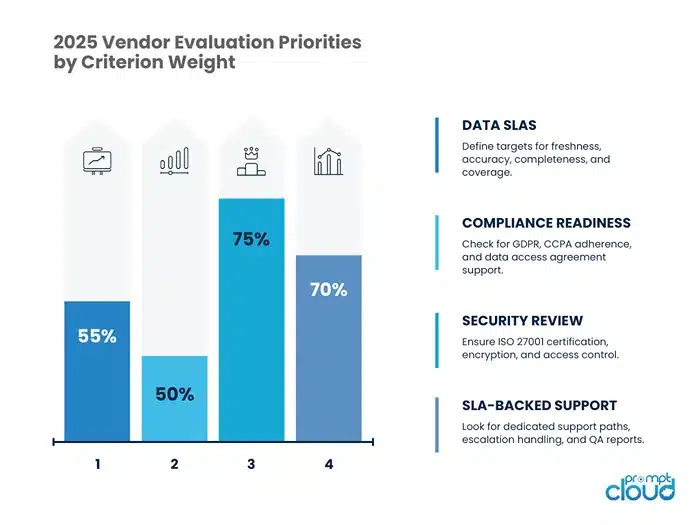
10 Non-Negotiable Criteria for Scraping Vendor Selection
When evaluating web scraping vendors, use this structured criteria table to compare apples to apples. These are the capabilities and guarantees enterprise buyers should insist on in 2026.
| Criteria | What to Look For |
| Data Quality SLAs | Defined targets for completeness, accuracy, freshness, and coverage |
| Security Review | ISO 27001 certification, encryption at rest/in transit, secure access controls |
| Compliance Readiness | GDPR, CCPA adherence; configurable jurisdictional data routing |
| Scalability | Ability to handle millions of pages/month, load-balanced infrastructure |
| Error Handling | Real-time alerts, retries, fallback pipelines, human-in-the-loop QA |
| Support SLAs | Guaranteed response times, dedicated account manager, escalation paths |
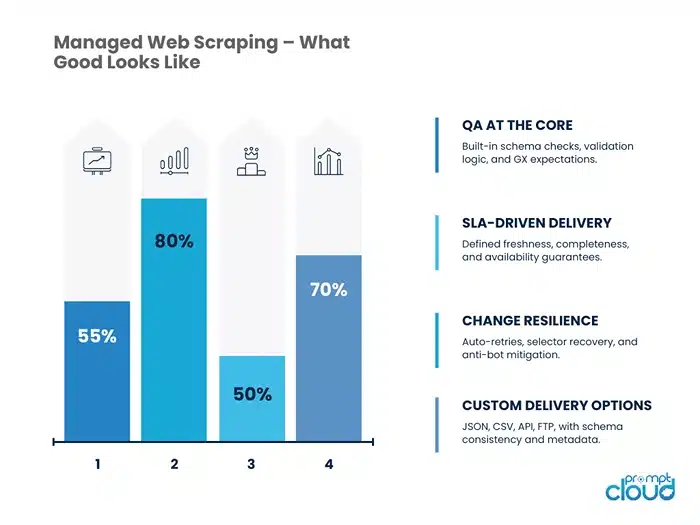
| Custom Delivery Formats | JSON, CSV, API, S3, FTP; schema consistency enforced |
| Change Resilience | Automated selector updates, drift detection, monitoring |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Transparent pricing model that includes retries, QA, compliance, infra overhead |
| Client References | Proven record with enterprise clients, use-case documentation |
This list forms the foundation of a high-quality web scraping RFP. Anything less means risking partial data, downtime, or compliance headaches.
Need reliable data that meets your quality thresholds?
If your scraping layer is already operating like production infrastructure, the conversation about ownership is worth having.
Common Pitfalls in Vendor Comparison (And What They Cost You)
Most teams start by comparing line items: pricing per URL, JavaScript support, speed, or format. These specs matter but they miss what breaks most scraping relationships in production. Here’s what often goes wrong:
Mistaking Low Cost for Low TCO
Vendors offering ultra-low rates often cut corners on retries, QA, or observability. You’ll spend more cleaning or fixing the data later than you saved upfront.
No QA or SLAs
Without field validation, schema checks, or freshness guarantees, you’re relying on hope. That leads to missing product specs, outdated prices, or broken stock status. Scraped data powers decisions; this data validation breakdown covers why broken schemas and unmonitored fields hurt accuracy.
No Error Transparency
When scrapers silently fail, bad data gets into dashboards. You need observability, alerts, and response workflows; not just success logs. If you care about pipeline reliability, this guide to real-time scraping architectures explains how QA fits into streaming data pipelines.
How to Structure a Web Scraping RFP?
1. Project Overview
Briefly describe:
- The data types you need (e.g., product listings, job posts, reviews)
- The frequency (daily, weekly, real-time)
- The volume (URLs per day/week/month)
- Intended use cases (pricing, ML training, analytics, etc.)
2. Technical Requirements
Ask vendors to confirm:
- Support for JavaScript-heavy sites
- Ability to handle dynamic URLs, pagination, geo-variations
- Data delivery formats and options (JSON, CSV, S3, API, FTP)
- Schema enforcement and change resilience
3. Data Quality Expectations
Set expectations around:
- Required fields (e.g., title, price, stock, rating)
- Validation logic (type, regex, cross-field logic)
- QA practices (manual sampling, GX expectations, SLA reporting)
To see QA in action, this automotive dataset page outlines how coverage and accuracy enable price benchmarking and part availability tracking.
4. Compliance & Legal Requirements
Vendors should address:
- How they handle robots.txt, site ToS, and terms of use
- GDPR/CCPA compliance
- Jurisdictional routing, audit logs, and consent policies
5. Security Practices
Request documentation or summaries of:
- ISO 27001 or equivalent certifications
- Encryption practices (at rest and in transit)
- Access controls, logging, and incident response
For field validation and rule-based schema checks, Great Expectations offers a powerful framework that works well with scraped datasets.
6. Support Model
Clarify:
- Support hours and timezone
- Escalation paths
- Dedicated account manager or point of contact
7. SLA Expectations
Include minimum requirements for:
- Freshness (e.g., 95% of prices updated in 30 mins)
- Completeness (e.g., 99% required fields filled)
- Accuracy (e.g., 99.5% valid prices, availability)
- Coverage (e.g., 98% of planned segments)
8. Pricing & TCO
Request a clear breakdown:
- Monthly or per-URL cost
- What’s included (retries, QA, support, setup)
- Any volume discounts, fixed delivery charges, or usage tiers
9. References & Case Studies
Ask for 1–2 enterprise client references in a similar domain or scale, plus links to relevant use cases.
What to Expect from a Managed Scraping Service in 2026
Choosing a managed web scraping provider means you’re not just paying for code or servers. You’re buying outcomes. That includes guaranteed delivery, QA accountability, and ongoing resilience as websites evolve.
Here’s what a top-tier managed scraping service should offer by default:
Data That’s Ready for Use
- Structured, validated, schema-consistent
- Delivered in your required format (CSV, JSON, API, S3)
- Mapped to your internal field logic or ingestion needs
Always-On QA Layer
- Schema validation and drift detection built in
- GX expectations or equivalent rule-based QA
- Manual QA sampling for business-critical fields
For ecommerce signals, this sentiment analysis playbook shows how quality review data supports better trend prediction.
Error Monitoring and Resilience
- Automated retries on failures (e.g., proxy errors, 429s)
- Headless fallbacks when pages fail in standard mode
- Annotated logs for debugging field issues, blank pages, or timeouts
Client Control Without Operational Overhead
- Modify target URLs, frequency, or fields with a support ticket
- Track scraping status and SLA compliance via dashboards
- Raise change requests without rebuilding pipelines
Human-in-the-Loop Support
- Escalations handled by engineers, not chatbots
- Annotator review when automation can’t catch layout or context changes
- Monthly QA and SLA reports with root-cause summaries
Understanding the Total Cost of Ownership
What to Include in TCO Calculations?
- Setup Fees: Initial crawler design, infrastructure, or onboarding charges.
- Crawl Costs: Per-URL or per-page charges. Confirm if retries count as extra.
- QA & Validation: Is schema validation, GX expectations, or manual QA included, or billed separately?
- Delivery Costs: Data hosting, API bandwidth, or file transfer fees.
- Compliance & Security: Some vendors charge for jurisdictional routing or secure storage.
- Support & SLA Coverage: Faster response times or dedicated managers may carry premium pricing.
- Change Management: Updates when a site changes layout or introduces new anti-bot measures.
The Risk of Ignoring TCO
- A low-cost scraper with no QA leads to expensive cleanup downstream.
- Vendors that don’t include retries or fallback pipelines may pass silent failures into your dataset.
- Weak compliance or security can expose you to fines, investigations, or customer trust issues.
The cheapest invoice is rarely the cheapest vendor. A complete TCO view keeps your procurement grounded in long-term costs, not short-term savings.
Security, Compliance, and Support Aren’t Optional
In 2026, enterprises can’t afford to treat web scraping like a gray-zone activity. With increased scrutiny around AI data sourcing, privacy compliance, and legal exposure, your vendor’s posture on security and compliance is a make-or-break factor.
Security Review Essentials
Your vendor should be able to demonstrate:
- ISO/IEC 27001 certification or equivalent for information security
- Encryption in transit and at rest (TLS 1.2+, AES-256)
- Role-based access control for your data pipelines
- Secure audit logs for delivery, validation, and error reporting
Compliance Guardrails
Modern scraping vendors must align with:
- GDPR, CCPA, and other regional data laws
- Respect for robots.txt and site terms of service
- Ability to route jobs through compliant jurisdictions
- Optional record annotation for downstream auditability
If your scraped data feeds into any regulated workflow—pricing models, consumer dashboards, AI training, etc.—you need more than boilerplate promises.
Support as a Contract, Not a Courtesy
Look for vendors that guarantee:
- 24–48 hour turnaround on critical tickets
- Dedicated account managers for enterprise clients
- Structured escalation paths tied to SLA breaches
- Monthly SLA + QA summaries with root cause breakdowns
This isn’t just “nice to have.” When data breaks, your business notices before the vendor does. Support isn’t reactive – it’s operational.
Using the RFP Template to Shortlist the Right Vendor
Most scraping projects fail silently—because no one asked the right questions up front. That’s what the RFP template is for: creating a level playing field so vendors must respond with operational clarity, not sales fluff.
How to Use the Template
- Customize the overview section with your use case, frequency, and delivery preferences
- Send the same RFP to all shortlisted vendors (3–5 max)
- Request written responses to all criteria, not just a pricing estimate
- Evaluate responses based on TCO, SLAs, QA structure, and compliance readiness
- Score each section—not just features but evidence of how failures are handled
What to Watch For in Responses
- Vague answers around QA, schema checks, or fallback handling
- No mention of SLAs or data freshness commitments
- Boilerplate language about “advanced tech” with no validation logic
- Lack of client references or real examples
The best vendors will respond with specificity, diagrams, client metrics, and real SLAs. That’s how you know they’re equipped for enterprise use.
The QA Feedback Loop: What Happens After the Sale?
Most vendor evaluations stop at delivery. But the real differentiator shows up after the contract is signed; when the site layout changes, product counts drop, or reviews stop showing up in the feed. A mature scraping vendor doesn’t just react to failures. They operationalize them.
What a QA Feedback Loop Should Include
- Detection: Schema drift, validation errors, null spikes, or missing pages trigger alerts
- Routing: Issues are assigned to the correct team—scraper, validator, or annotator
- Resolution: Automated retries, selector updates, or human QA flagging are applied
- Documentation: Errors are logged and tagged with issue type, site, and resolution status
- Learning: Recurring issues are turned into new rules (e.g., GX expectations, regex, fallback selectors)
Scraped data powers decisions; this data validation breakdown covers why broken schemas and unmonitored fields hurt accuracy.
Why It Matters
- Reduces human cleanup downstream
- Protects model training from silent corruption
- Builds trust with internal teams and clients
- Speeds up issue resolution over time
You’re not buying a perfect scraper. You’re buying a self-healing pipeline—and that requires closed-loop QA, not just “monitoring.”
What 2026 Buyers Expect from Web Scraping Vendors
1. AI-Driven Resilience
The best vendors have moved past rigid extractors. They now use AI-based field detection, layout prediction, and retraining workflows to:
- Spot when a field vanishes or changes label
- Visually re-anchor selectors based on page structure
- Adapt across domains with minimal manual tuning
This ensures data continuity even when sites update designs frequently. Ask vendors for real examples of zero-touch extractor retraining.
2. Multi-Modal Scraping Support
Modern scraping demands more than HTML. Vendors should support:
- OCR for product images and price tags
- PDF parsing for catalogues, policy docs, and rate cards
- Embedded JSON extraction for review sections, feature flags, or availability metadata
If your use case involves rich content, request a test run on an image-heavy or PDF-driven site. Static HTML skills won’t be enough.
3. Schema Evolution and Version Control
Your internal systems change. New KPIs emerge. Fields shift meaning. Best-in-class vendors offer:
- Versioned schema support
- Change logs per field or extractor
- Backward-compatible delivery options (to avoid breaking ingestion)
Ask: What happens when we need to add or rename a field mid-cycle?
Ethical, Legal, and Licensing Maturity in Vendor Selection
Compliance is now a dealbreaker. In 2026, your scraping vendor must treat robots.txt, data usage policies, and regional data laws as foundational—not optional.
Data Access Agreements (DAAs)
Websites increasingly publish DAAs (Data Access Agreements) that legally bind what can be scraped, stored, or redistributed. Your vendor should:
- Track and honor DAAs for critical targets
- Route jobs via compliant proxies or jurisdictions
- Maintain audit logs for legal traceability
Failure to follow DAAs could result in contractual liability or account bans, not just tech blockers.
Legal Positioning and Risk Sharing
Ask your vendor:
- How do you handle websites that block scraping via legal means, not tech?
- Will you sign a data use indemnity clause or handle takedown notices?
- Can you deliver jurisdiction-aware routes (e.g. EU-only processing)?
You want a vendor who understands web scraping law and ethics, not one who simply “tries their luck with rotating proxies.”
Use Case Stress Tests to Vet Vendor Capabilities
Pricing, reviews, sentiment, and document scraping aren’t just “scrapeable”, they push a vendor’s QA, resilience, and anti-bot systems to their limits. These use cases help surface those limits early.
Challenge-Based Vendor Assessment
| Use Case | What It Tests | What to Ask |
| 10K product prices across 50 sites | Schema consistency, freshness, retry logic | Can your platform ensure 95% coverage + freshness in under 30 minutes? |
| Amazon reviews | JS rendering, pagination handling, language noise | How do you handle lazy loading, region switches, and UGC filtering? |
| Policy PDFs and rate sheets | PDF parsing, layout logic, tabular inference | Can you convert table-based PDFs into structured JSON or CSV? |
| Reddit / Trustpilot sentiment | Unstructured text, spam detection, emotional tone | What NLP or filtering do you apply before labeling sentiment? |
| Localized listings | Geo-targeting, proxy accuracy, content variance | How do you match country-specific content while preventing false duplicates? |
Vendors that fail these tests may be fine today, but they’ll struggle when your use case evolves. Ask for a live walkthrough of a similar project; not just a capabilities deck. The gap between “we support that” and “we’ve solved that under pressure” is where projects fail.
The Stakes Are Higher So Are the Expectations
In 2026, web data is no longer a convenience—it’s a competitive edge. Poor vendor choices lead to downstream chaos: broken dashboards, misinformed decisions, corrupted models, and compliance risks. That’s why vendor selection must shift from “scraper capability” to operational trust, legal defensibility, and pipeline fit.
Treat your scraping vendor the way you’d treat any other data provider or infrastructure partner. Demand clarity. Demand SLAs. Demand visibility. And most importantly, build a selection process that protects you not just today, but six months into production.
With that, let’s answer some of the most common buyer questions.
Need reliable data that meets your quality thresholds?
If your scraping layer is already operating like production infrastructure, the conversation about ownership is worth having.
FAQs
1. What should be the top priority when selecting a scraping vendor?
Look beyond surface-level specs. Prioritize operational reliability: data quality SLAs, compliance guarantees, QA layers, and long-term support capabilities.
2. What’s the difference between a scraper and a managed scraping service?
A scraper is just code. A managed service includes error handling, schema validation, retries, monitoring, delivery infrastructure, and human support—delivering data, not just extraction.
3. How do I know if a vendor is legally compliant?
Check for GDPR/CCPA adherence, respect for robots.txt, and readiness to operate under DAAs. Ask for documentation, legal reviews, and jurisdictional controls.
4. Can I use the same vendor for PDF, image, and review scraping?
Only if they support multi-modal scraping. Ask for examples of successful OCR, PDF parsing, and unstructured sentiment data processing across large volumes.
5. What if my schema or use case changes later?
Your vendor should support versioned schemas, change logs, and backward compatibility. Flexible delivery and modular architecture are critical for evolving use cases.


















