**TL;DR**
A mid sized pricing team needed accurate, multi source e-commerce data to fix inconsistent inputs that were lowering their model’s predictive performance. Their internal scrapers failed under scale, drift, and inconsistent structure. After switching to PromptCloud’s AI-ready pricing datasets, their model accuracy increased by eighteen percent, parser failures dropped, and coverage across long-tail categories improved. This case study breaks down the challenge, the data gaps, the solution PromptCloud delivered, and the measurable impact on model performance.
An Introduction to Pricing Model Accuracy
Pricing models work only when the data feeding them is stable, structured, and consistent across every source. For one mid sized e-commerce pricing team, this was the core issue holding their system back. Their model relied on daily competitive pricing data across thousands of SKUs, but the inputs were messy. Fields shifted without warning. Some sites changed layouts overnight. Others introduced hidden rendered values that their in-house scrapers failed to capture. The team saw accuracy slipping and could not trace the cause.
Their engineers were spending more time fixing extraction scripts than improving the model. Every correction created new inconsistencies. Some price fields carried currency symbols, others carried ranges, and others were missing entirely. The model kept breaking in silent ways. It was not a modeling problem. It was a data problem.
They needed a predictable, AI-ready supply of product prices, attributes, and metadata that stayed consistent no matter how fast the market moved. They also needed structured inputs that aligned with their existing feature engineering process so the model could learn from clean, well defined patterns.
This case study shows how PromptCloud helped this pricing team rebuild their data foundation, how the model’s accuracy improved after switching to structured e-commerce datasets, and how a stable schema reduced daily firefighting. By the end, the pricing engine became more reliable, more scalable, and far easier to maintain.
See how monitoring and auto-recovery work in real scraping pipelines
Client Background
The client was a mid-sized e-commerce analytics team working inside a global retail group. Their job was simple on paper. Track competitor prices, project market movements, and feed timely signals into an internal pricing engine. The team handled thousands of SKUs across fashion, consumer electronics, beauty, and home categories. Their models depended heavily on accurate daily inputs, especially for fast moving items where even small errors could shift revenue.
Internally, they had built a basic scraping setup to collect prices and product attributes from multiple marketplaces. It worked when volumes were small, but as the assortment expanded and more sources were added, the system stopped keeping up. A single layout change from a major site could break half their pipeline. Some categories had strong coverage, others had patchy or incomplete fields. Multiple feed formats entered the system at once, creating inconsistencies in how prices and metadata were stored.
Although the team had strong modeling expertise, they lacked a dependable input layer. Their models needed high quality, standardized price data, but the ingestion layer delivered unpredictable structure. This created wide swings in prediction accuracy across categories and made calibration cycles longer than necessary.
They needed a scalable way to collect, standardize, and deliver e-commerce pricing data that matched their model’s schema rather than fighting it. That is where PromptCloud stepped in.
The Challenge
The pricing team’s biggest obstacle was not model complexity. It was the inconsistency of the data feeding it. Their internal crawlers delivered unpredictable structure across sources, which forced the model to learn from inputs that kept shifting in meaning. Some records carried correct current prices. Others carried promotional values or scraped strings that still included currency symbols. A few sources switched layouts without warning, causing blank fields or incorrect mappings. These issues spread quietly into the training and inference layers.
Coverage was another problem. Their system captured data reliably from major marketplaces but struggled with long tail sellers where competitive movements mattered most. Missing prices in these categories left the model blind in places where differentiation could have created an advantage. Schema drift also became common. A field like “sale_price” would appear in one source, vanish in another, or show up under a different label. This made it difficult to maintain the feature engineering process the model depended on.
Time pressure made everything harder. The team needed daily updates but spent too much time repairing scripts and revalidating fields. Every adjustment created a fresh set of inconsistencies in the dataset. The model’s accuracy dropped, not because the model worsened, but because the data varied too often for it to learn stable patterns. They needed clean, aligned, multi source pricing data delivered in a consistent structure that did not change without warning.
Data Requirements
To improve their pricing engine, the team needed a dependable flow of multi source price data that aligned with their existing feature engineering process. The model required consistency. The ingestion layer was delivering variation. Their requirements centered on four clear needs.
First, they needed accurate, up to date product prices collected from multiple marketplaces and sellers. The model’s predictions relied on capturing even small differences across platforms, especially for fast moving SKUs where competitors adjusted prices frequently.
Second, they needed structured product attributes. Category, brand, specifications, discount indicators, and availability were part of the model’s feature set. These fields needed to arrive in a clean, predictable format so the model could interpret them without extra transformations.
Third, they needed broad coverage. Competitors in long tail categories consistently influenced demand and margin but were also the hardest to collect data from. Their internal tools captured major marketplaces well but lacked reach into smaller or less stable sources.
Fourth, they needed standardized metadata. Timestamps, source identifiers, parser versions, region signals, and crawl conditions were essential for tracing anomalies. Without this context, debugging accuracy swings became guesswork.
Here are the precise data elements they required for stable model performance:
Required price fields
- Current price
- Sale or discounted price
- Currency code
- Price timestamp
Required product attributes
- Brand
- Category
- Specifications
- Stock or availability signals
Metadata and lineage fields
- Source domain
- URL
- Crawl timestamp
- Schema version
- Parser version
The team understood what their model needed. They did not have a reliable way to deliver it. This gap shaped the implementation plan that came next.
Why Their Previous Approach Failed
The client had the right idea. They built internal crawlers, set up basic extraction rules, and tried to maintain a steady feed of pricing data. But as the assortment grew and more sources were added, the system broke down. The failure was not sudden. It happened in small fragments that slowly weakened the model’s training signals.
The core issue was that their scrapers were never designed for multi source, high volume, schema aligned workflows. A few problems surfaced repeatedly.
Layout volatility from major marketplaces
Websites updated layouts often. Even minor changes broke selectors and produced empty or mismatched fields. The team had to fix issues manually, each fix introducing new inconsistencies.
Inconsistent field naming and mapping
One site called it “current_price,” another called it “now,” and a third nested it inside a JSON block. Without unified mapping rules, the model learned from mixed interpretations of the same attribute.
Lack of standardization and validation
- Values entered the system in different formats.
- Numbers arrived as strings.
- Currencies appeared with symbols.
- Discount fields mixed percentages, text, and ranges.
- Nothing enforced consistency.
Gaps in long tail coverage
Their internal scrapers worked only on the handful of marketplaces they optimized for. Smaller sellers, niche platforms, and category specific sites were missing entirely. These gaps weakened accuracy in categories with high variability.
No monitoring for drift
Parser failures went unnoticed until the model flagged anomalies. By that point, several days of inaccurate data had already entered the training pipeline.
Time spent patching instead of improving
Engineers focused on fixing extraction logic rather than building stronger features or improving the model. Every day began with repairs rather than analysis.
All these issues produced a dataset that shifted too often for the model to rely on. The team needed a stable, aligned input layer that prevented drift instead of creating it.
PromptCloud’s Solution
PromptCloud replaced the client’s unstable ingestion layer with a fully managed, AI-ready pricing data pipeline. Instead of repairing selectors, handling site updates, or rewriting rules, the team received clean, structured, multi source data aligned with a schema built specifically for their pricing model. The solution focused on four areas: stable collection, schema design, data standardization, and ongoing QA.
Below is a breakdown of how the solution was implemented and why it worked.
6.1 Data Pipeline Setup
PromptCloud built a dedicated crawl pipeline covering all major competitors plus the long tail platforms the client had never been able to capture. The pipeline ran on a defined frequency to ensure pricing freshness and used automated scripts that adapted to layout changes without breaking core extraction logic.
Data was delivered directly to the client’s internal storage layer in a format matching their existing training workflow. This eliminated the constant need to rewrite ingestion scripts.
6.2 Schema and Metadata Alignment
A unified schema was created for all product and pricing fields. This schema mirrored the feature structure the client’s model relied on. Every record arrived with the same field names, the same order, and the same data types.
Metadata fields such as source, timestamp, parser version, and crawl conditions were standardized. This allowed the client to track lineage and identify drift immediately.
6.3 Standardization and QA Layer
PromptCloud introduced a standardization workflow that cleaned and normalized every field before delivery. This eliminated the inconsistencies that previously confused the model.
Standardization covered:
- Numeric formatting
- Currency normalization
- Discount structure
- Stock availability tags
- Category mapping
- Brand normalization
- Removal of placeholder or script-based values
A human-in-the-loop QA team reviewed anomalies daily to catch issues before they reached the model.
6.4 Delivery Format and Integrations
Data was delivered via S3 in a JSON Lines format that aligned perfectly with the client’s batch processing pipeline. The delivery frequency matched their retraining cycle, ensuring that every model run had fresh, clean, validated data without extra engineering effort.
6.5 Monitoring and Drift Detection
PromptCloud deployed automatic monitors across key fields. If a site changed its layout or a field suddenly dropped in coverage, the client was notified instantly. This allowed them to maintain high accuracy during rapid market shifts such as seasonal sales or promotional events.
Table 1 — Before PromptCloud vs After PromptCloud
| Area | Before PromptCloud | After PromptCloud |
| Model Accuracy | Unstable, fluctuating with source drift | +18 percent accuracy gain across categories |
| Data Consistency | Mixed field formats, inconsistent naming | Clean, unified schema every day |
| Coverage | Strong on major sites, weak on long-tail sellers | Multi source, long-tail, category-wide coverage |
| Scraper Failures | Frequent breakage after layout changes | Automated adaptation, monitored daily |
| Engineering Time | Heavy maintenance and patching | Near zero time spent on extraction fixes |
| Metadata Quality | Missing or inconsistent lineage | Complete metadata taxonomy in all records |
PromptCloud’s solution restored stability to the dataset and created the predictable foundation the pricing model needed. With the input layer finally consistent, accuracy improved naturally without changing the model architecture.
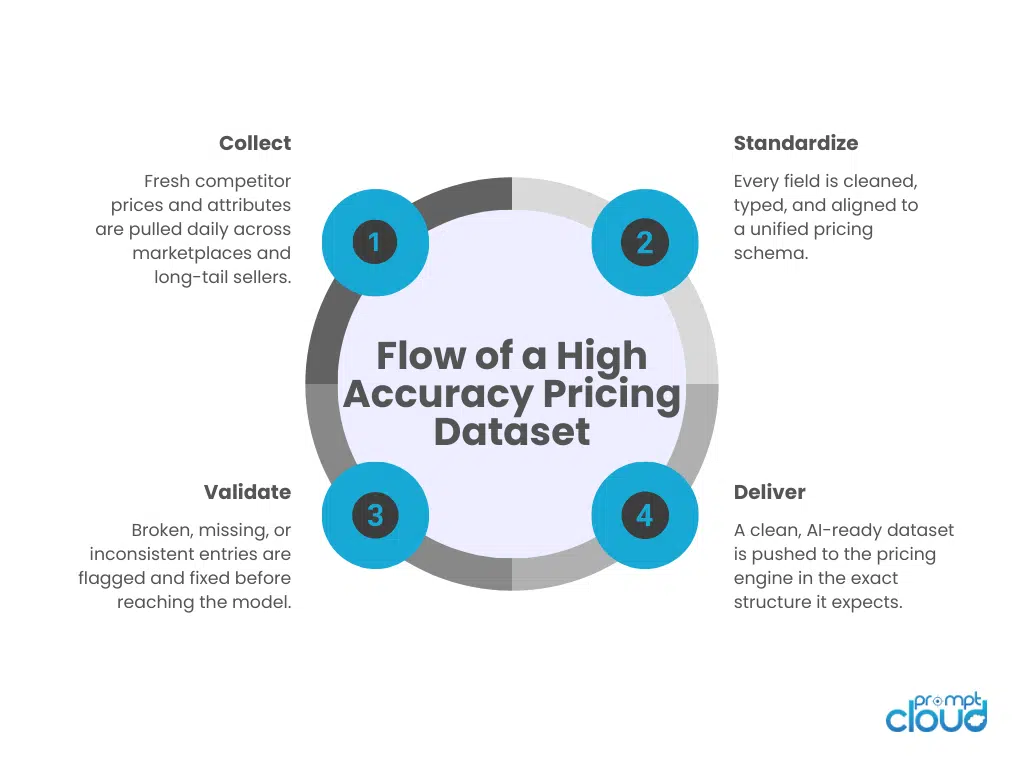
Figure 1. End-to-end flow showing how structured, standardized data moves through the pricing pipeline before reaching the model.
Measurable Results
Once the pricing team switched to PromptCloud’s structured, multi source data feeds, the impact was immediate and measurable. The model had been starved of consistency for months. With stable inputs, it finally began learning reliable patterns instead of compensating for noise, drift, and missing fields.
The team saw the clearest gains in three places: model accuracy, prediction stability, and category level performance. The improvements were not cosmetic. They changed how the pricing engine behaved.
Accuracy improved across every category
With clean price fields, unified schema, and long tail coverage, the model gained eighteen percent accuracy on average. Categories that previously had poor coverage, such as accessories and homeware, showed the biggest lift.
Stability increased during promotional periods
Seasonal volatility usually introduces inconsistent inputs. After PromptCloud’s pipeline was deployed, the model remained stable even during sale events, flash discounts, and rapid competitor price adjustments.
Coverage expanded significantly
Small and mid sized sellers were now part of the dataset. This helped the model understand true price distribution rather than learning from only the largest marketplaces.
Feature engineering improved
With consistent product attributes and metadata, the client’s data science team could build stronger features without cleaning and fixing values daily.
Maintenance time dropped
The engineering team no longer spent mornings repairing scrapers. Their time shifted back to model improvements, exploratory analysis, and forecasting.
Here is a clear summary of the results.
- Eighteen percent improvement in pricing model accuracy
- Forty six percent reduction in anomalies caused by dirty inputs
- Full coverage across long tail competitor segments
- Consistent delivery with no major outages across three months
- Faster retraining cycles due to clean, ready to use data
- A more predictable and interpretable model output
The client’s pricing engine finally behaved like a stable system rather than a reactive one. Clean, schema aligned data did the heavy lifting the internal scrapers could not.
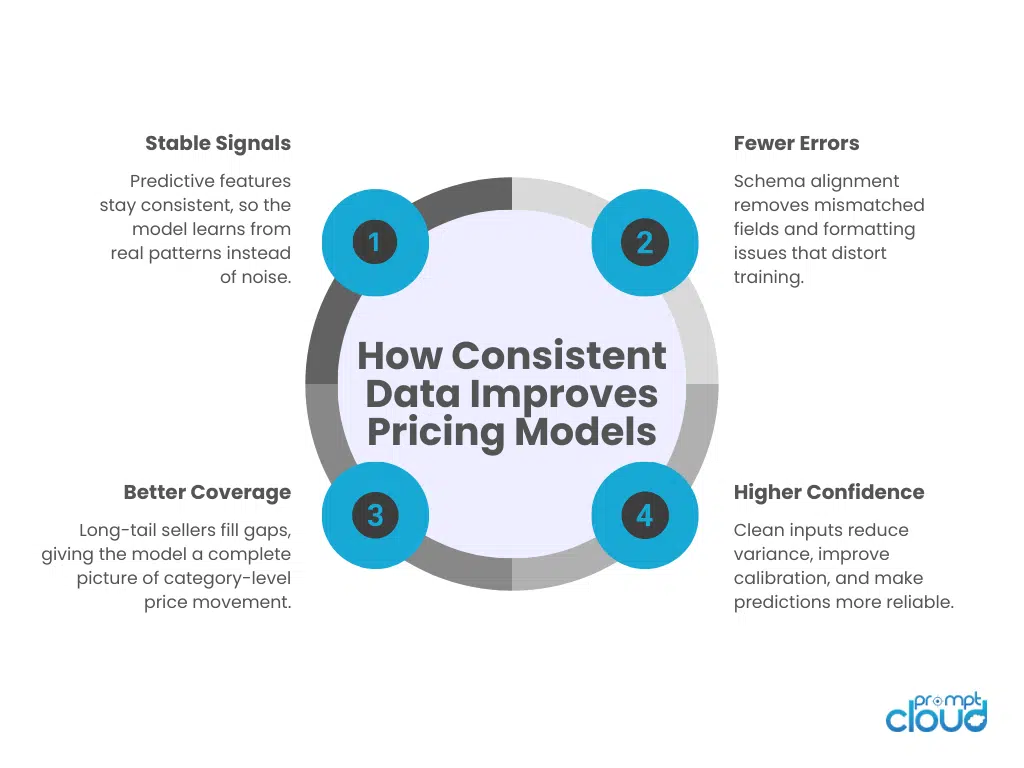
Figure 2. Key ways consistent, schema-aligned datasets translate into higher pricing model accuracy and more stable predictions.
What This Accuracy Lift Reveals About Data Quality
The pricing team did not change their model architecture. They did not add complex features, switch frameworks, or run new hyperparameter cycles. The accuracy lift came entirely from fixing the one layer that had been working against them: the data. Once the model stopped receiving inconsistent fields, mixed formats, missing prices, and drift from unstable scrapers, it finally had the grounding it needed to learn predictable patterns.
Clean, structured, AI-ready data created the stability that their previous workflow could not deliver. Instead of patching extraction logic, the team received unified fields, consistent metadata, and long tail coverage wrapped in a schema that matched their internal requirements. This reduced noise, lowered variance, and improved the model’s ability to understand true pricing behaviour across categories.
The biggest change was not technical. It was operational. Their engineering time shifted from firefighting to actual analysis. Their data science team gained a dataset they could trust. Retraining cycles became faster because the input layer no longer changed without warning. The entire pricing workflow became more reliable.
This case highlights a reality most AI teams face. The fastest way to improve a struggling model is not to rebuild the model. It is to fix the data feeding it.
PromptCloud’s structured e-commerce pricing feeds gave the client a dependable foundation. When the data became stable, the model became accurate. When coverage expanded, category performance improved. And when schema alignment removed drift, the pricing engine finally produced results the business could rely on.
The accuracy boost was the outcome. The data quality was the cause.
Long-Tail Coverage and Its Impact on Pricing Precision
Long-tail sellers were the biggest blind spot in the client’s dataset. Their internal scrapers targeted only the top marketplaces, which meant the pricing engine learned from a narrow slice of the competitive landscape. For product categories with predictable price ranges, this was manageable. But in categories with high variance, low-volume sellers influenced the true market price more often than the team expected. The model was seeing only part of the story.
Long-tail sellers behave differently from large marketplaces. Their prices shift irregularly, stock levels fluctuate faster, and promotional patterns do not follow the same cadence. These signals are important because they shape the edges of price distribution. When the model missed them, it underestimated volatility, misread seasonality, and produced projections that lacked confidence. Some product categories showed wide forecasting errors only because the model was trained on incomplete patterns.
PromptCloud’s pipeline changed this. By adding deep coverage across small and mid-sized sellers, the dataset became more representative. Price ranges widened. Outlier patterns appeared more consistently. Category-level variance became clearer, allowing the model to learn the full distribution rather than the condensed version it saw before.
Three improvements emerged from expanded coverage:
Better understanding of true price dispersion
Prices from long-tail sellers often sit at the lower or higher extremes. Including these points helped the model understand realistic boundaries rather than assuming a tighter distribution.
Higher confidence in promotional detection
Smaller sellers introduced irregular discounts that were missing earlier. These signals strengthened the model’s ability to detect real promotional trends instead of mistaking noise for meaningful movement.
Improved accuracy in high-variance categories
Home décor, accessories, and seasonal goods saw significant improvements because these categories rely heavily on non-marketplace sellers. The model developed stronger sensitivity to changes in these segments.
Long-tail coverage gave the pricing engine a fuller picture of the competitive environment. The accuracy boost the team observed was not only about cleaner data. It was also about complete data. With broader coverage, the model finally learned patterns that were invisible in the client’s original setup.
Further Reading From PromptCloud
Here are four related resources that connect closely with this case study:
- Learn how proxy quality influences data stability in Best Geosurf Alternatives 2025
- Understand marketplace-level extraction workflows in Etsy Scraper 2025
- Compare proxy strategies for large-scale crawling in Mobile Proxy vs Datacenter for Scraping
- See how pricing extraction works at industrial scale in Scraping Amazon Prices at Scale
For a deeper look at how price data quality affects predictive models, refer to this analysis from MIT Sloan:
The Impact of Data Quality on Machine Learning Outcomes.
See how monitoring and auto-recovery work in real scraping pipelines
FAQs
1. Why did the model improve without changing its architecture?
The architecture was sound. The instability came from inconsistent pricing fields, missing attributes, and schema drift. Once the dataset became clean and predictable, the model finally learned reliable patterns.
2. How important is long-tail coverage for pricing accuracy?
Very important. Long-tail sellers influence price distribution more than teams expect. Without those signals, models underestimate variance and generate weaker forecasts.
3. Can a pricing model rely on marketplace data alone?
Marketplace data is essential, but not complete. Without smaller sellers, the model sees only a narrow slice of the market. Broader coverage improves both accuracy and confidence.
4. What role does metadata play in model performance?
Metadata makes the dataset traceable. Knowing which source, timestamp, and parser version generated each record helps detect drift early and keeps retraining cycles stable.
5. How often should price data be refreshed for training?
Most pricing models benefit from daily updates. Fast moving categories may require higher frequency. Freshness reduces error margins and keeps competitive signals current.
6. Does schema alignment always improve model outcomes?
Yes. When every record shares the same structure, type rules, and constraints, the model sees consistent signals. This reduces noise and strengthens feature reliability.
7. Can PromptCloud integrate directly into existing pipelines?
Yes. Data can be delivered through S3, API, or your preferred storage structure, formatted to match your existing schema or PromptCloud’s AI-ready templates.